Configuring WEP or WPA Encryption on a Networked Mac
Posted by DAISUKE 13.6.51 at 09:09
You can set up either WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol) or WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) encryption to make your wireless network more secure. WPA encryption is much more secure than WEP encryption. You should use WPA-PSK or WPA Personal encryption on your home wireless network unless you have computers that only support WEP encryption.
Setting up WEP encryption
Use the following steps to set up WEP encryption on a Mac:
1. Choose Apple --> System Preferences to open the System Preferences window.
2. Click the Network icon to open the Network dialog box.
3. Choose AirPort in the Show menu and choose Preferred Networks in the By Default, Join menu.
4. Select a network in the list of networks and click Edit.
5. In the Wireless Security menu, choose a WEP option. Choose ASCII or HEX as appropriate for your network.
If you're not sure whether to choose ASCII or HEX, or if your network uses 64-bit WEP encryption, choose WEP Password instead.
6. Enter the WEP key in the password text box.
7. Click OK and then quit Network Preferences.
To make sure you're typing the WEP key correctly, temporarily select the Show Password check box so that you can see the characters you are typing. Make sure no one is looking over your shoulder when you do this.
Configuring WPA encryption
Follow these steps to configure WPA encryption:
1. Choose Apple --> System Preferences to open the System Preferences window.
2. Click the Network icon to open the Network dialog box.
3. Choose AirPort in the Show drop-down menu and choose Preferred Networks in the By Default, Join menu.
4. Select a network in the list of networks and click Edit.
5. In the Wireless Security menu, choose WPA Personal.
WPA Personal is equivalent to WPA-PSK, which is used by many wireless access points. WPA Enterprise requires that a RADIUS server be running on your network, something your home network is not likely to have.
6. Enter the WPA password in the password text box.
7. Click OK and then quit Network Preferences.
Special Wi-Fi Considerations for Macs
Posted by DAISUKE at 09:04
Macintosh computers have been at the forefront of wireless networking with AirPort, Apple's name for the Wi-Fi technology used in modern Macs. Most new Macs have AirPort Extreme — a newer, faster version of AirPort — built right in. If you buy a new Mac without AirPort Extreme you may be able to install a card. By using AirPort or AirPort Extreme, you can connect your Mac to any 802.11b/g Wi-Fi network.
Some Macs —such as the Mac mini — can only be upgraded by an Apple repair professional. When you buy a new Mac, spend a little extra money to get an AirPort Extreme card preinstalled — it's worth it.
Installing an AirPort card in an iBook
Follow these steps to install an AirPort card in an iBook:
1. Shut down your iBook and remove the battery.
To remove the battery, use a coin to turn the lock screw on the bottom of the iBook to the unlocked position.
2. On the front of your iBook, push the keyboard release tabs (see Figure 1) towards the front of the iBook and gently lift the keyboard out of the chassis. You don't need to disconnect the keyboard; simply rest it upside down on the touch pad.
Figure 1: The keyboard release tabs.
3. Locate the built-in AirPort antenna in the space provided for the AirPort card.
If you don't see a space for the AirPort card, your iBook either is not compatible with AirPort or it already has AirPort installed.
4. Connect the antenna to the antenna port on the AirPort card.
5. Insert the AirPort card into the slot, ensuring that the connector pins seat firmly in the AirPort card socket.
Do not force the card into position. If the AirPort card and the port on your computer don't match, you probably have the wrong kind of card for your iBook model.
6. Seat the AirPort card wire retention clasp and replace the keyboard and battery.
Installing an AirPort card in an eMac
Follow these steps to install an AirPort card in an eMac:
1. Open the DVD-ROM disc tray and leave it open.
2. Shut down your computer and make sure that the power is off.
Disconnect the power cable to make sure that the computer doesn't accidentally turn on while you are installing the card.
3. Remove the two Philips-head screws on the cover inside the disc tray to reveal the AirPort card slot (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: The AirPort card slot.
4. Disconnect the antenna from the cover and then press the antenna into the AirPort card's antenna port.
5. Insert the AirPort card firmly into the slot until it seats and then reinstall the cover inside the disc tray.
Connecting to a Wi-Fi access point
To connect to a Wi-Fi access point, follow these steps:
1. If AirPort isn't already enabled, click the AirPort icon on the menu bar in the upper-right corner of the screen and choose Turn AirPort On.
2. Click the AirPort icon in the menu bar again and choose Other to connect to a new Wi-Fi network.
If the access point is set to broadcast its SSID, it may appear in the list of available networks in the AirPort menu. If you see the network to which you want to connect listed, click its name.
3. In the resulting Closed Network dialog box, enter the network's SSID in the Network Name text box.
4. Choose a Wireless Security method as needed for the network.
5. Click OK to connect to the network.
6. Check the status and signal strength of the Wi-Fi network by clicking the AirPort icon in the menu bar and choosing Open Internet Connect.
Managing Wi-Fi networks
Follow these steps to manage your Wi-Fi network:
1. Choose Apple --> System Preferences to open the System Preferences window.
2. Click the Network icon to open the Network dialog box.
3. Choose AirPort in the Show menu to reveal AirPort settings.
4. In the By Default, Join menu, choose Preferred Networks.
5. In the resulting list, rearrange the order by clicking and dragging networks up or down in the list.
6. To remove a network from the list, click the network to select it and then click the Remove (-) button.
7. Select a network and choose Edit to change encryption keys and other network details for a given network.
8. When you are done making changes, click the Apply Now button and then quit System Preferences.
To update the AirPort software, choose Apple --> Software Update to run the Software Update. Download and install any necessary updates to your computer.
Configuring a DHCP Client on a Windows PC or Mac
Posted by DAISUKE at 09:01
If you have one computer that connects directly to the Internet through a modem, you can share that computer's Internet connection using Windows ICS (Internet Connection Sharing). When you set up ICS, your computer — called the host computer — becomes a DHCP server for the rest of the network. After the host is set up, the rest of the computers on your network must be set up as clients. ICS clients can be Windows PCs or Macintosh computers.
Configuring a Windows PC as a DHCP client
Use these steps to configure a Windows PC as a DHCP client:
1. Open the Windows Control Panel and then double-click the Network Connections icon to open a list of network connections.
2. Double-click your current connection to the network.
3. In the resulting Status dialog box, click Properties.
4. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click the Properties button.
5. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, select the Obtain an IP Address Automatically option.
6. Select the Obtain DNS server address automatically option.
7. Click OK and close all open dialog boxes.
When you set your computer to obtain an IP address automatically, it gets the address from either your router's built-in DHCP server, or from an ICS Host on another computer. You may need to restart your computer for your changes to take effect.
Configuring a Mac as a DHCP client
Follow these steps to configure a Mac as a DHCP client:
1. Open System Preferences from the Apple menu and click the Network icon.
2. In the resulting Network control panel, click the Show menu drop-down arrow and choose the network connection you use to connect to the network.
If your computer connects to the network using the built-in Ethernet network port, choose Built-In Ethernet in the Show menu. If you connect using an AirPort Card, choose AirPort in the Show menu instead.
3. Click the TCP/IP tab.
4. Click the Configure menu drop-down arrow and choose Using DHCP.
5. Click the Apply Now button and then close the Network control panel.
6. Press Command+Q to quit System Preferences and then restart your computer.
If you're using a portable Mac, you can use it to connect to several different networks. For example, at home you may connect it to your home network using an Ethernet cable, but at Wi-Fi hotspots you may connect using AirPort instead. Use the Location menu at the top of the Network control panel to specify connection settings for different network locations.
Macintosh OS X can obtain an IP address automatically from a DHCP server built in to any router, or from a Windows PC running Internet Connection Sharing.
Logging into a Windows PC from a Mac (and Vice Versa)
Posted by DAISUKE at 08:59
If your network is all Windows or all Macintosh, sharing files back and forth is easy. But if you have a mix of Windows PCs and Macs, you'll have to go through a special log in procedure before you can share files and folders.
Logging in to a Windows PC from a Mac
Follow these steps to log in to a Windows PC from a Mac:
1. In Mac OS 10.2 or 10.3, choose Go --> Connect to Server. In OS 10.4 and later, open Finder and then click Network.
You may need to wait several seconds for the list of computers to be populated. In some cases you may also see a Windows workgroup name listed. If you see the workgroup, double-click it to open it.
2. In the Connect to Server window (OS 10.2 or 10.3), click the name of the computer to which you want to connect. In OS 10.4 and later, double-click the folder bearing the name of your Windows workgroup to browse the workgroup.
By default, newer Macs are set with the default workgroup name "Workgroup." This probably isn't the correct workgroup name for your Windows workgroup. To check the workgroup name for your Windows network, go to a Windows PC, right-click the My Computer icon, and choose Properties from the menu that appears. In the System Properties window, click the Computer Name tab to bring it to the front. The workgroup name is listed on this tab. Click OK or Cancel to close the System Properties window.
3. Double-click the computer to which you want to connect.
4. In the resulting SMB/CIFS Filesystem Authentication dialog box, type a username and password for an account on the Windows computer to which you are trying to connect and click OK.
If you only want to access shared items on the Windows PC, just enter any user name and leave the password field empty. Doing so gives you access to public items on the Windows PC.
5. Choose a volume that you want to mount.
Items in the list of things you can mount include shared folders, as well as folders owned by the user account you are using to log in to the Windows PC.
6. Click OK. The selected item mounts on your computer as if it were a disk drive or volume.
7. Double-click the network volume's desktop icon to browse its contents.
In Mac OS 10.4 and later, you can also access mounted volumes directly from Finder. In the Finder window, simply click the volume's icon in the upper-left corner.
8. Click and drag files to copy them between computers.
If you only want to access shared folders on the Windows PC, enter any user name in Step 4 and leave the password blank. You will still be able to log in to the Windows PC, although you will only be able to access shared folders.
Logging in to a Mac from a Windows PC
Follow these steps to log in to a Mac from a Windows PC:
1. Open My Network Places from the Windows Start menu.
2. Click View Workgroup Computers under Network Tasks on the left side of the screen to display the list of workgroup computers on the right.
Macintosh computers may have the word Samba in front of their names in the list of workgroup computers. Samba is the Mac OS X software that allows Windows and Macintosh PCs to network with each other.
3. Double-click a Macintosh computer in the list.
4. In the resulting Connect To dialog box, enter the user name and password for the Windows user account on the Mac.
5. Click OK to log in. After you are logged in, you can see a list of available files and folders on the Mac.
You can only access items that are owned by the Windows user account on the Mac. If you want to share items with other user accounts on the Mac, store them in the Public folder. Each user's Public folder in Mac OS X is shared with other users.
Creating a User Account on Your Wi-Fi Network
Posted by DAISUKE at 08:53
Chances are you have two main reasons for setting up a home network: you want to share an Internet connection between your computers and you want to be able to copy files between computers. If you use a Mac and want to allow access to the network from Windows PCs, you must first create a Windows user account.
Follow these steps on the Mac to create the Windows user account:
1. Open System Preferences from the Apple menu.
2. Click the Accounts icon to open the Accounts window.
3. Click New User (OS 10.3 and earlier) or the plus sign in the lower-left corner of the Accounts window (OS 10.4 and later).
4. Enter a name, short name, and password for the user (see Figure 1).
For example, you can name the account Windows to help you remember the purpose of the account later.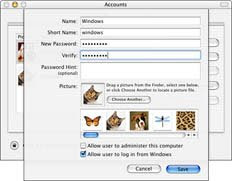
Figure 1: Name the Windows user account.
5. Select the Allow User to Log In from Windows check box if you see it.
As the name implies, this option enables users to log in using this account on Windows PCs. This option is not available (or required) in newer versions of Mac OS X.
6. Click Save or Create Account (depending on your OS X version) to save the new user account. The Windows account now appears in the list of user accounts, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: The Windows account appears in the list.
Because Mac OS X is based on UNIX, user account names and passwords are case sensitive. Make sure that Windows users on your network know this, because if the user name is "Windows" and they try to log on using "windows," the log in attempt will be unsuccessful.
Sharing Folders on Wi-Fi Networks
Posted by DAISUKE at 08:52
Computer files are organized into folders on your hard drive. In Windows and Mac OS X, access to those folders is strictly controlled. If you own a folder, other computers on your network — and even other users on the same computer — can't access it. To copy files back and forth over the network, you can share folders with others.
Sharing a folder in Windows
Follow these steps to set up folder sharing in Windows:
1. Choose Start --> All Programs --> Accessories --> Communications --> Network Connections.
2. In the Network Connections window, right-click your network connection and choose Properties from the menu that appears.
3. In the Network Connection Properties dialog box, select the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks check box.
File and Printer Sharing may already be enabled on your computer, but you should double-check it to make sure.
4. Click OK to close the dialog box.
5. Open My Computer or Windows Explorer.
6. Locate the Shared Documents folder. Right-click the Shared Documents folder and choose Sharing and Security from the menu that appears.
7. In the resulting Properties dialog box, select the Share This Folder on the Network check box.
8. Type a descriptive name for the folder in the Share Name field.
9. Click OK to close the Properties dialog box.
10. To share files or folders, copy them into the Shared Documents folder using My Computer or Windows Explorer.
To create a new subfolder in the Shared Documents folder, open Shared Documents and then choose File --> New --> Folder. Give the new folder a descriptive name.
Accessing a shared network folder in Windows
To access a shared networks folder in Windows, follow these steps:
1. Choose Start --> My Network Places.
You can also access My Network Places from My Computer or Windows Explorer. In My Computer, click My Network Places under Other Places on the left side of the screen. In Windows Explorer, click My Network Places near the bottom of the folder tree on the left side of the screen.
2. In the My Network Places window that appears, double-click the network place that you want to open.
If you don't see a network folder that you think should be available, make sure that the computer containing the network folder is turned on and connected to the network. Also, double-check the file sharing settings on the other computer.
3. Browse the network folder.
4. To copy an item to a shared network folder, simply click and drag it to the shared folder's window. (You can also use Cut, Copy, and Paste commands when browsing shared network drives.)
When you share a folder, anyone on your network can access it. Do not store private or sensitive files in shared folders.
Enabling file sharing in OS X
If you are using a Mac, follow these steps to enable file sharing in Mac OS X:
1. Open System Preferences from the Apple menu and then click Sharing.
2. In the resulting Sharing control panel, provide a descriptive name for your computer. (Other computers will see this name over the network.)
3. Select the Personal File Sharing check box. If you will be sharing folders with Windows PCs, check the Windows File Sharing option as well.
4. Close the Sharing control panel.
These steps assume that you have Mac OS Version 10.2 or better. Windows File Sharing is only available in Mac OS 10.2 or better. Sharing files between Windows and older versions of Mac OS requires special third-party programs.
Changing the workgroup name in OS X
Follow these steps to change the workgroup name in Mac OS X.
1. Open the Applications folder on your hard drive and then open the Utilities subfolder.
2. Double-click the Directory Access utility to open it.
3. Click the lock icon at the bottom of the Directory Access utility and then enter an administrator name and password.
4. Select SMB/CIFS on the Services tab and then click the Configure button.
5. Enter your Windows workgroup name in the Workgroup field and click OK.